In accordance with the EU's implementation of the Personal Data Protection Act, we are committed to safeguarding your personal information and providing you control over it. We have updated and will regularly update our Privacy Policy to comply with this personal data protection law. Please refer to our latest Privacy Statement.
This website uses cookies to enhance your browsing experience. To learn more about how this website uses cookies, please click here.
Latest News
28.Jul.2025
Application
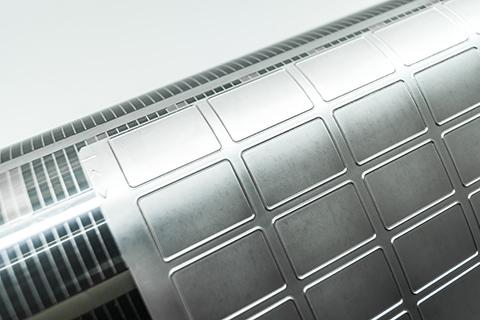
Die Cutting Rule Materials & Heat Treatment Technologies
1. Intro: Brief overview of die cutting and its importance in various industries. The role of blade materials and heat treatment in ensuring precision and longevity.
b. High-Speed Steel (HSS): Contains tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium for improved hardness and heat resistance. Suitable for high-speed operations and materials requiring precise cuts.
c. Tool Steel (D2, A2, M2, etc.)
b. Cryogenic Treatment: Sub-zero cooling process to refine the steel’s microstructure. Enhances wear resistance and toughness.
c. Coating Technologies: Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), and Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings.
Benefits include reduced friction, extended lifespan, and better corrosion resistance.
b. Comparison table of different materials and their best-use scenarios.
c. How different materials affect sharpness, durability, and efficiency.
d. Case studies of industries using specific blade materials.
b. When it makes sense to invest in premium die cutting blades for high-volume production vs. cost-effective solutions for lower-demand applications.
b. Encouraging readers to consult experts or explore high-quality die cutting solutions.
c. Hung Shuh’s expertise in providing die cutting materials and die cutting solutions.
2. Common Materials Used in Die Cutting Blades
a. High-Carbon Steel (HCS): Affordable and commonly used for general-purpose cutting. Pros & Cons: Good sharpness but wears out faster than high-alloy steels.b. High-Speed Steel (HSS): Contains tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium for improved hardness and heat resistance. Suitable for high-speed operations and materials requiring precise cuts.
c. Tool Steel (D2, A2, M2, etc.)
3.Heat Treatment Technologies for Die Cutting Blades
a. Hardening and Tempering: Increases hardness while maintaining flexibility to prevent brittleness. Common temperature ranges and their effects on blade performance.b. Cryogenic Treatment: Sub-zero cooling process to refine the steel’s microstructure. Enhances wear resistance and toughness.
c. Coating Technologies: Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), and Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings.
Benefits include reduced friction, extended lifespan, and better corrosion resistance.
4.How to Choose the Right Blade Material and Heat Treatment
a. Factors to consider: Cutting application, material thickness, production speed, and budget.b. Comparison table of different materials and their best-use scenarios.
c. How different materials affect sharpness, durability, and efficiency.
d. Case studies of industries using specific blade materials.
5.Cost vs. Performance Considerations
a. A comparison of initial costs vs. long-term savings when choosing higher-grade materials.b. When it makes sense to invest in premium die cutting blades for high-volume production vs. cost-effective solutions for lower-demand applications.
6.Making Smart Investments in Die Cutting Technology
a. How to choose the best blade material and heat treatment for specific applications.b. Encouraging readers to consult experts or explore high-quality die cutting solutions.
c. Hung Shuh’s expertise in providing die cutting materials and die cutting solutions.
Other
15
Dec.2025
Application
Thick Material and High Rule - Applications and Techniques
28
Jul.2025
Application
Thermoforming Die Cutting Applications & Industry Insights
28
Jul.2025
Application