In accordance with the EU's implementation of the Personal Data Protection Act, we are committed to safeguarding your personal information and providing you control over it. We have updated and will regularly update our Privacy Policy to comply with this personal data protection law. Please refer to our latest Privacy Statement.
This website uses cookies to enhance your browsing experience. To learn more about how this website uses cookies, please click here.
Latest News
29.Jan.2026
Material Knowledge
What Does the "M" in JIS Standard "SK85-M" Stand For?
Understanding MIGAKI Special Steel (JISG3311) vs. SK85 (JIS G4401)
" What does the 'M' in SK85-M mean? "
This is one of the most frequently askedquestions by automotive component manufacturers and precision engineers when wehandle MIGAKI special steel.
The answer is : the "M" standsfor "MIGAKI (steel with a polished-like surface finish)".
Here, “polished-like” does not mean that the steel has been mechanicallypolished. Rather, after cold rolling, the steel strip achieves a smoothersurface and a bright finish resembling polished steel, which is why it isreferred to as MIGAKI.
But what exactly is MIGAKI?
And how does the commonly known SK85 differ from SK85-M?
In this article, we explain the differencesbetween JIS standards and why
SK85-M (JIS G3311) is preferred for precision components.
What is "MIGAKI"?
"MIGAKI" does not simply mean a polished surface.
According to JIS G3311, MIGAKI special steel refers to:
-
Hot-rolled steel as the base material
-
Cold-rolled to significantly improve thickness accuracy and surface quality
This process results in:
-
High precision thickness tolerance
-
Uniform and stable surface condition
-
Dimensional stability after forming
Steel processed in this way is what we call SK85-M.
Same SK85 Name, Different Standards
Standard SK85 (JIS G4401)
When SK85 is mentioned generally, it often refers to JIS G4401: Carbon Tool Steel.
This standard primarily specifies:
-
Chemical composition
-
Hardness after quenching
-
Surface quality and thickness precision are not the main focus.
SK85-M (JIS G3311)
In contrast, SK85-M that we handle is:
-
Standard: JIS G3311 (MIGAKI Special Steel)
-
Composition: Equivalent to SK85
-
Form: Cold-rolled steel strip
Features:
-
High-precision thickness tolerance
-
Superior surface finish (polished-like appearance)
-
Designed for precision forming applications
Even though both are called SK85, their applications, quality level, and processing suitability are clearly different.
Key Quality Features of Our SK85-M
-
Fully compliant with JIS G3311 chemical composition
-
Thickness tolerance strictly according to JIS G3311
-
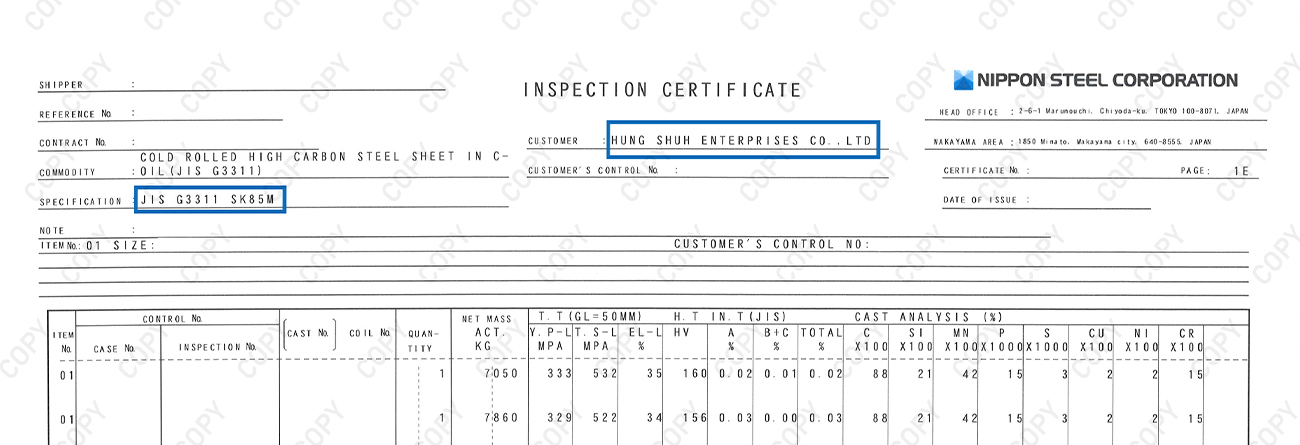
Material certificate clearly indicates " JIS G3311"
This level of quality, officially recognized by the standard, is a differentiator compared to competitors.
For automotive parts and precision spring components, where performance is sensitive to thickness variation, this is especially critical.
Applications of SK85-M (JIS G3311) in Automotive Parts
SK85-M is primarily used for thin steel strip parts formed from cold-rolled steel, where material properties directly impact performance.
Representative applications include:
-
Clutch components (leaf/plate springs): Require stable thickness tolerance and dimensional accuracy after forming
-
Horn (vibration diaphragm): Require uniform thickness and hardness for stable vibration characteristics and fatigue resistance
-
Washers (thin plate/disc springs): High-volume use requires consistent quality across production batches
Note: Coil springs made from wire or parts manufactured by non-strip methods are excluded.
Conclusion: Understanding the "M" Improves Material Selection
The "M" in SK85-M = MIGAKI (steel with a polished-like surface finish)
It represents:
-
High-precision thickness control achieved by cold rolling
-
Strict requirements for surface quality and dimensional stability
-
Design concept intended for precision component applications
Even though both are called SK85,
SK85 according to JIS G4401 and
SK85-M according to JIS G3311
are different in purpose and quality level.
For precision components, confirming the JIS standard behind the material is more important than just the material name.
The material from Hung Shuh is classified as G3311 and can help resolve the issue. If you have any questions, don't hesitate to get in touch with us.
Additional note: Nippon Steel Mill Sheet.
Additional note:
Obtaining and continuously maintaining certification under JIS G3311 (Polished Special Steel Strip) is by no means an easy task.
JIS certification does not merely confirm that chemical composition or dimensional tolerances meet the standard. It also requires comprehensive evaluation of the entire manufacturing process, quality control systems, inspection methods, and their consistent execution in daily production. Regular factory audits and product testing are conducted to verify long-term stability and reproducibility across production lots, making JIS certification a true indicator of manufacturing discipline.
The JIS standard itself is Japan’s national industrial standard defining quality, performance, and testing methods for industrial products. It is currently known as Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS), a name adopted following a legal revision in 2019. While the name has changed, its fundamental role remains the same: to serve as a common foundation supporting the reliability of Japanese manufacturing.
The purpose of such standards is not only to set minimum requirements, but also to ensure that products exhibit consistent and repeatable performance, regardless of when or where they are used.
From this perspective, compliance with JIS G3311 represents far more than formal conformity to a specification.
It demonstrates that, even for **high-carbon steel strip—one of the most demanding materials to control—**the manufacturer possesses the technical capability and quality management systems necessary to deliver stable quality across the entire length and width of each coil.
In press forming operations, where yield, die adjustment, and dimensional stability after heat treatment are critical, these differences in material quality and quality control often become clearly visible in actual production results.
Other
03
Nov.2025
Material Knowledge
Hardness Conversion Table
27
Jan.2026
Material Knowledge